Integrating AcraTranslator into infrastructure #
How AcraTranslator works #
Refer to AcraTranslator architecture page to find out deep description of internals and how it works.
AcraTranslator installation #
There are multiple ways to install AcraTranslator.
You will also need utilities like acra-keys that come along.
Key generation #
You will need some keys in order to launch AcraTranslator, so let’s do it first.
The first one will be used to protect all the other keys,
it should be base64-encoded and passed to Acra services in ACRA_MASTER_KEY environment variable.
Like this: ACRA_MASTER_KEY="$(cat /tmp/master_key | base64)" acra-server ...
The second key is responsible for data encryption. There are actually more kinds of keys, read more about that on Acra keys inventory.
It is also possible to store keys in a Redis database, see Scalable KV storages.
Note about Client ID #
When generating a key, you will always have to bind it with a Cliend ID or Zone ID (zones are deprecated since 0.94.0, will be removed in 0.95.0). AcraTranslator distinguishes requests by Client ID and uses different encryption keys for different client ID.
Architecture and DataFlow of AcraTranslator-based infrastructure #
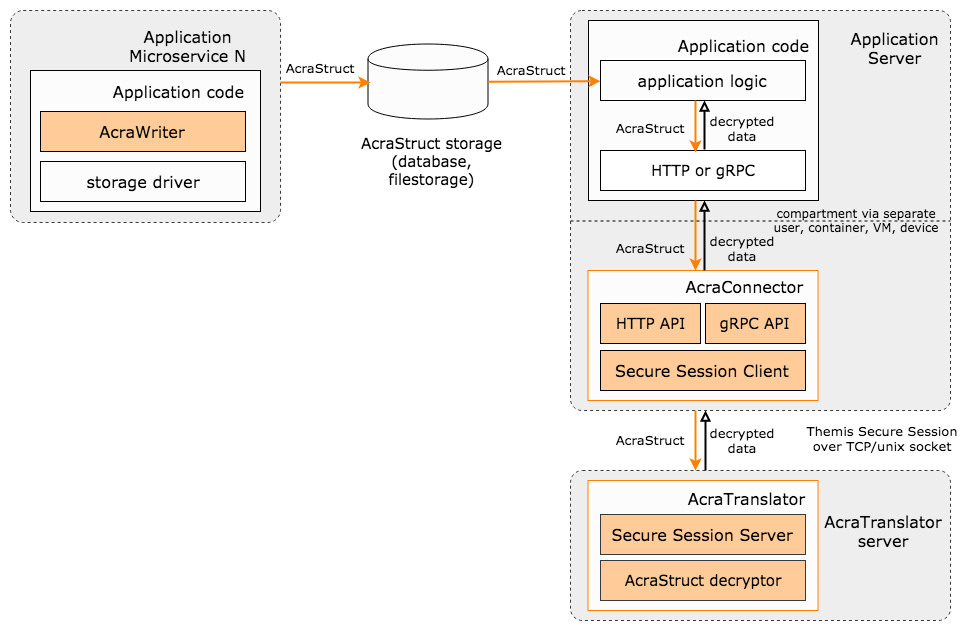
Acra design values simplicity as much as security.
- The application sends AcraStructs or AcraBlocks via HTTP or gRPC API.
- AcraConnector sends that request to AcraTranslator using Themis Secure Session (socket protection protocol).
- AcraTranslator accepts the request and attempts to decrypt an AcraStruct or AcraBlock. If the decryption is successful, it sends the resulting plaintext in the response. If decryption fails, AcraTranslator sends out a decryption error.
- AcraTranslator returns the data to AcraConnector (via Themis Secure Session), which in turn returns it to the application.
AcraTranslator reads decryption keys from key folder and stores them encrypted in memory. It uses LRU cache to increase performance by keeping only actively used keys in memory. The size of LRU cache can be configured depending on your server’s load.
Note: AcraTranslator supports ability to use [TLS] as encryption channel instead of Themis Secure Session. In such case, you don’t need to use AcraConnector, but you should manage all your TLS certificates manually.
AcraTranslator configuration #
Refer to AcraTranslator configuration page.
AcraConnector (optional) #
AcraConnector is as intermediate proxy between the application and AcraTranslator. Why would you need yet another proxy? Well, there are a couple of reasons:
- Providing secure transport to AcraTranslator: if application does not support TLS, communicates with AcraTranslator on remote host, and you want to ensure the communication channel is safe
- Specifying which Client ID to use: when using TLS, you will have to use client IDs derived from some certificate properties (such as serial number), but with AcraConnector you can use whatever ID you want by simply setting configuration option when launching AcraConnector
AcraConnector usually lives on the same host as the application, but is isolated a bit (running as different user, in separate docker container and so on).
Read more in Client side encryption with AcraConnector and AcraWriter.
Changes on application side #
- Teach application to work with AcraTranslator API. Generate code for gRPC client or write own to work with HTTP API
- Make sure application will accept TLS certificate configured in AcraTranslator in case of usage TLS as transport protection
- Deploy and configure AcraConnector close to application if you can’t use TLS and prefer using Themis Secure Session instead as transport protection.
AcraWriter integration (optional) #
One of the things available in enterprise edition is
part of SDK called AcraWriter
that allows data encryption right inside the application for Encrypt operations via gRPC/HTTP API calls.
Poison records #
If the client application is hacked, and the attacker is trying to decrypt all the data, you can detect it using poison records.
AcraTranslator (similarly as AcraServer) has ability to detect poison records and stop executing the request, preventing the data from leaking to an untrusted destination. To learn more about AcraTranslator cmd configuration you can refer here.
Read more #
- Storage and data model implications lists current limitations introduced when using AcraTranslator
- Encryption docs describes encryption configuration more precisely, describes how AcraTranslator encrypts/decrypts data on the fly
- docker-compose examples may give you various ideas about AcraTranslator integration in docker environment