Data flow #
So, which Acra services and components you need? Depends on your use case! Let’s see some typical dataflows.
Not sure what is AcraServer or AcraTranslator? Get back to Acra-in-depth / Architecture section.
Simple data flow schemas #
Simplest version with SQL proxy #
App ↔︎ AcraServer ↔︎ SQL database
It’s a classic scenario: AcraServer sits between your application (or database-facing microservice) and the actual SQL database, encrypting and decrypting data, providing masking/tokenization, even filtering SQL requests if you like.
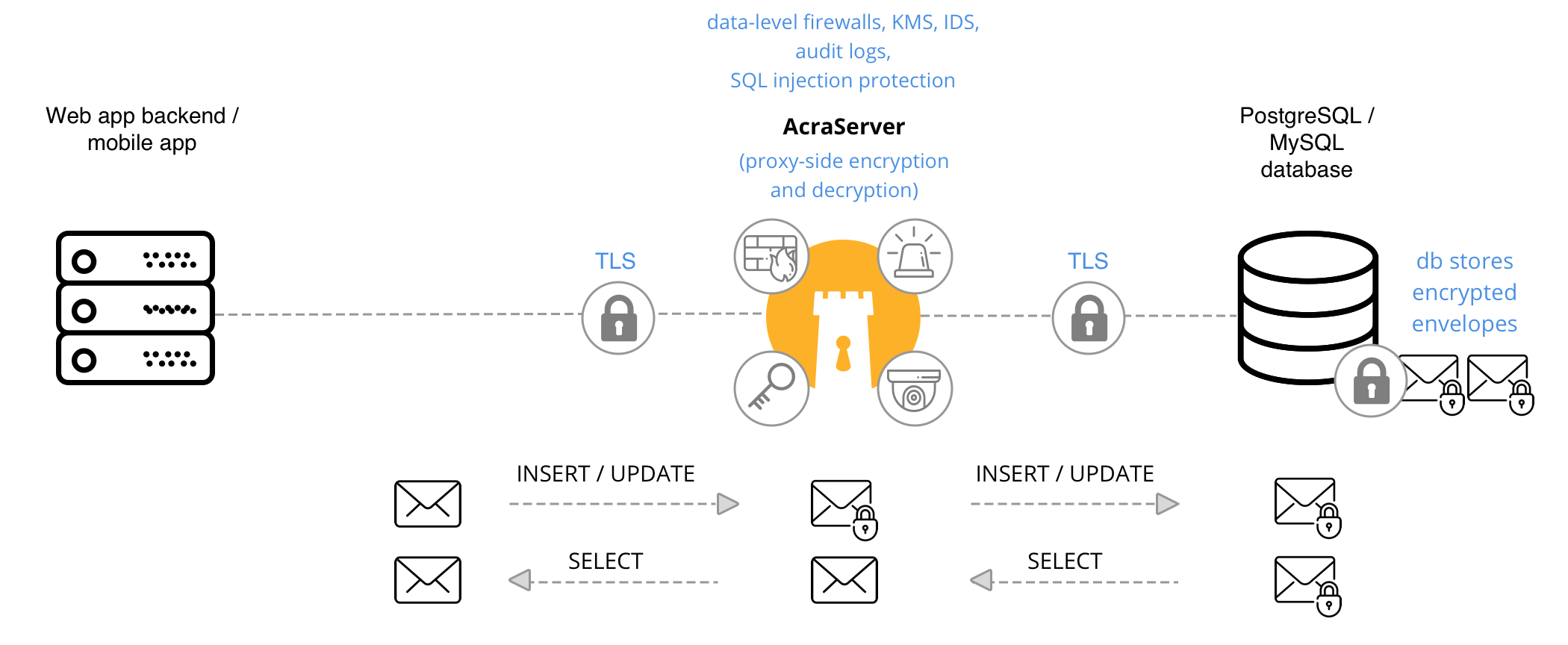
When to use #
If you are using MySQL/PostgreSQL database and want to integrate Acra “transparently” for your app.
Which components to use #
AcraServer, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and TLS transport encryption.
Writing #
Application → AcraServer → SQL database
Application sends data to database through AcraServer in Transparent encryption mode. You configure AcraServer indicating which fields to encrypt/decrypt/mask/tokenize.
All data manipulations like encryption, searchable encryption, tokenization, masking applied on AcraServer side before sending data to database.
If SQL firewall is configured, AcraServer applies SQL request filtering.
Reading #
Application → AcraServer → SQL database → AcraServer → Application
Application requests data from a database through AcraServer. AcraServer transparently decrypts/detokenizes/unmasks data and passes it to the application.
Simplest version with API service #
App ↔︎ AcraTranslator, App ↔︎ Datastore
Another classic scenario: your application speaks to the API service to encrypt/decrypt/mask/unmask/tokenize/detokenize data, and then stores it in the datastore or sends to another application.
This scenario is also known as Encryption-as-a-service.
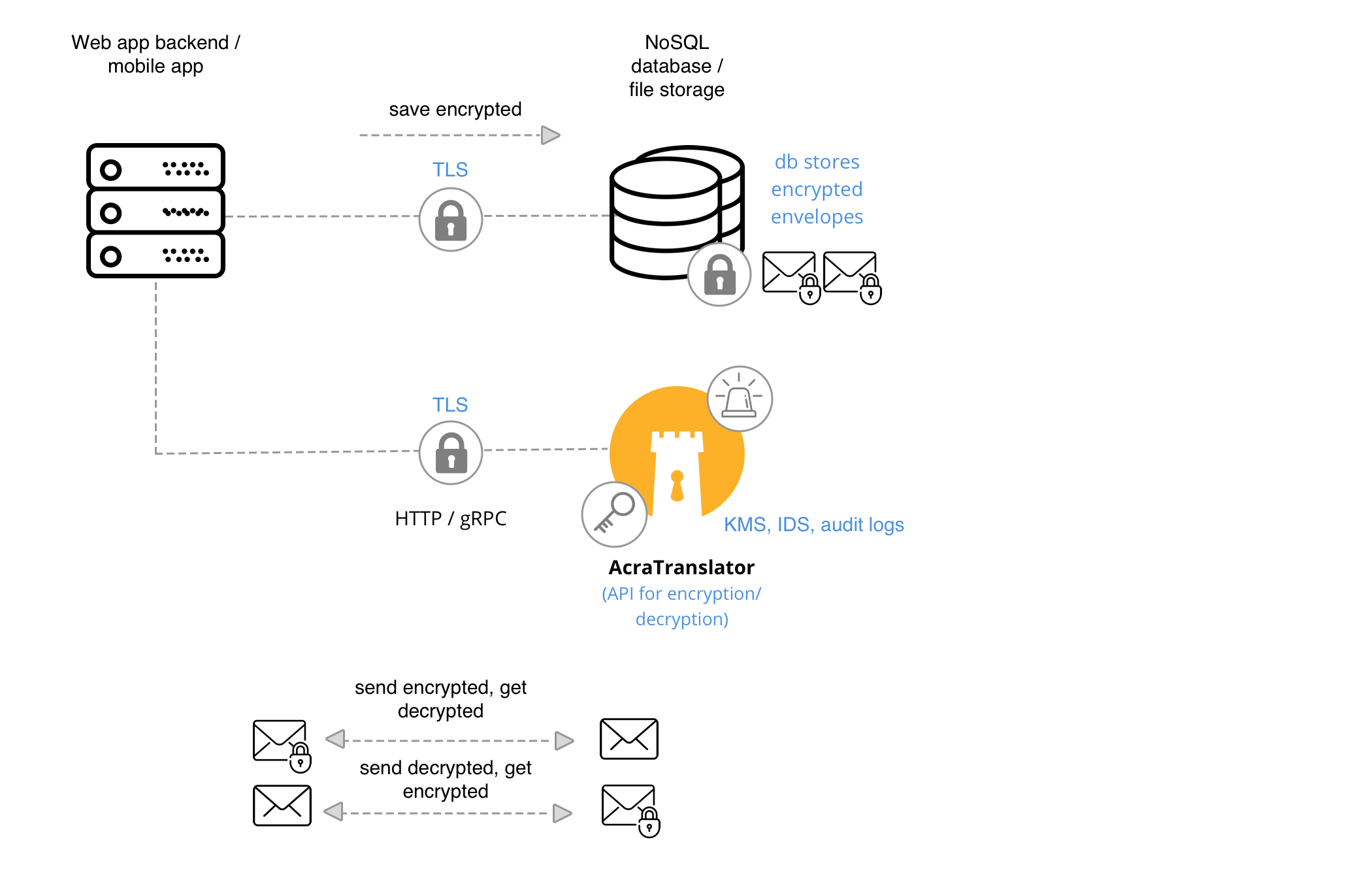
When to use #
If you are using NoSQL / KV datastore and want your application to be responsible for calling encryption service and then storing the data.
Which components to use #
AcraTranslator, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and TLS transport encryption.
Writing #
Application → AcraTranslator → Application → Datastore
Application knows which fields to encrypt/mask/tokenize. Application sends these fields to AcraTranslator via gRPC or HTTP API. AcraTranslator performs required function and sends protected data back to the app. The app is responsible to store the received data.
Reading #
Application → Datastore → Application → AcraTranslator → Application
Application reads encrypted data from the storage or the other application and needs to decrypt/demask/detokenize it. Application sends these fields to AcraTranslator via gRPC or HTTP API. AcraTranslator performs required function and sends original data back to the app. The app is responsible to use the data.
AnyProxy #
App ↔︎ DAO (↔︎ AT or AS) ↔︎ other API
Application needs to access sensitive data, which is stored separately encrypted. Application sends requests to DAO (data access object), that is responsible for reading the encrypted data from the datastore, decrypting it using AcraTranslator and sending it back to the requested application.
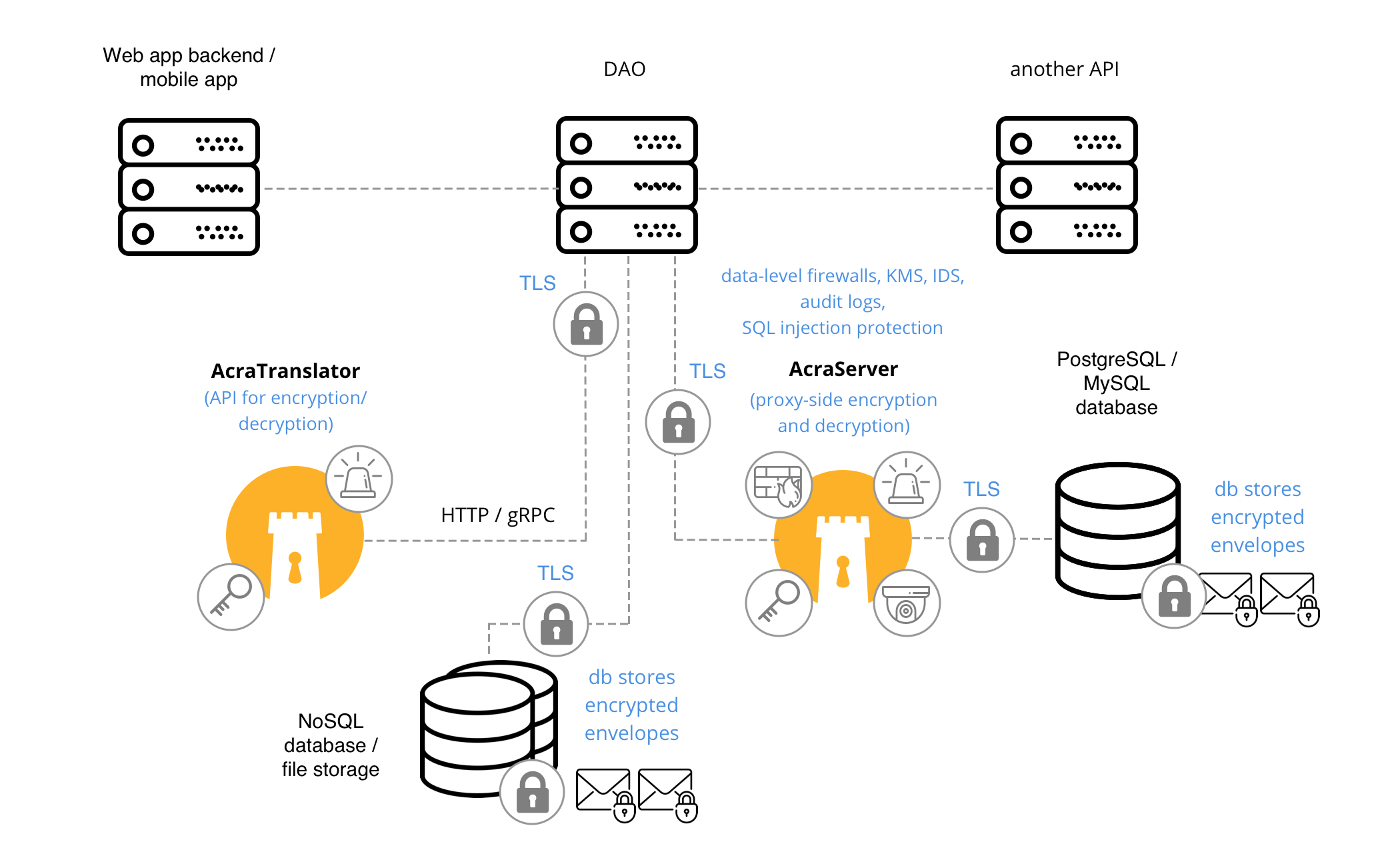
When to use #
When sensitive data is isolated into separate database / table, and there are several applications that need to access it in a plaintext: typical apps and BI tools, for example. Instead of teaching these tools to talk to Acra, you create a separate service – DAO, that is responsible for talking to Acra and encrypting/decrypting data. Other apps just talk to DAO.
Depending on the database that you use, DAO can talk to AcraServer (for SQL databases) or AcraTranslator (NoSQL/KV).
Which components to use #
AnyProxy, AcraTranslator or AcraServer, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and TLS transport encryption.
Writing #
Application → DAO ↔︎ [AcraTranslator, AcraServer, Datastore] → Application
Application sends sensitive fields to DAO to protect. DAO communicates with AcraServer/AcraTranslator to encrypt/mask/tokenize the fields and stores them in a database/datastore.
Reading #
Application → DAO ↔︎ [AcraTranslator, AcraServer, Datastore] → Application
Application asks DAO for sensitive fields in a plaintext. DAO reads encrypted/masked/tokenized fields from the database/datastore, and communicates with AcraServer/AcraTranslator to decrypt/demask/untokenize the fields. DAO receives plaintext fields and sends them back to the application.
Long data lifecycle #
Acra was built to accompany sensitive data lifecycle in large, microservice-driven applications. So you can use APIs inside applications and proxies between some services and databases to build pretty sophisticated lifecycles.
End-to-end encrypted dataflow #
App [AcraWriter] ↔︎ Datastore ↔︎ App [AcraReader]
Application uses AcraWriter SDK to encrypt data on application side, and then stores data in a database/datastore. Application reads encrypted data and uses AcraRead SDK to decrypt it.

When to use #
When some parts of the dataflow should be end-to-end encrypted. We strongly advise to combine this approach with typical dataflow using AcraServer/AcraTranslator - meaning, that some apps will use AcraServer/AcraTranslator as designed, while some apps will process data on client-side only.
Which components to use #
AcraWriter, AcraReader, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and TLS transport encryption.
Writing #
Application [AcraWriter] → Datastore
Application locally encrypts sensitive data using AcraWriter. The app is responsible for accessing Acra’s encryption keys. The app is responsible to store protected data.
Reading #
Application → Datastore → Application [AcraReader]
Application reads encrypted data from the datastore, locally decrypts it using AcraReader. The app is responsible for accessing Acra’s decryption keys.
Client-side encryption, server-side decryption #
App [AcraWriter] ↔︎ AcraServer ↔︎ SQL database
Application uses AcraWriter SDK to encrypt data on application side, and sends it to the database through AcraServer. Application reads the data through AcraServer that decrypts it.

When to use #
When the system will benefit from client-side encryption and security controls provided by AcraServer. One application can send encrypted data (“writer”), other can read decrypted data through AcraServer (“readers”).
Which components to use #
AcraWriter, AcraServer, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and TLS transport encryption.
Writing #
Application [AcraWriter] → AcraServer → SQL database
Application locally encrypts sensitive data using AcraWriter. The app is responsible for accessing Acra’s encryption keys. Then the app sends data to the database directly or via AcraServer. AcraServer will detected encrypted data and won’t encrypt it twice.
Reading #
Application → AcraServer → SQL database → AcraServer → Application
Application requests data from a database through AcraServer. AcraServer transparently decrypts/detokenizes/unmasks data and passes it to the application.
Using AcraConnector and AcraServer #
App ↔︎ AcraConnector ↔︎ AcraServer ↔︎ SQL database
AcraConnector is deprecated since 0.91.0 and is not available since 0.92.0.
Similar to the classic scenario the simplest dataflow with AcraServer, but the application uses AcraConnector for transport encryption.
AcraConnector uses TLS or Themis Secure Session to provide additional transport encryption and mutual authentication for apps that work in hostile environments.

When to use #
When client-side application works in a hostile environment and extra transport security is required.
Which components to use #
AcraServer, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and AcraConnector.
Writing #
Application → AcraConnector → AcraServer → SQL database
Application sends plaintext data through AcraConnector. AcraConnector uses powerful transport encryption to protect data in a plaintext. AcraServer works in Transparent encryption mode. AcraServer performs encryption, searchable encryption, masking, tokenization.
Reading #
Application → AcraConnector → AcraServer → SQL database → AcraServer → AcraConnector → Application
Application requests data from a database through AcraServer. AcraServer transparently decrypts/detokenizes/unmasks data and passes it safely to the application using AcraConnector.
Using AcraWriter, AcraConnector and AcraServer #
App [AcraWriter] ↔︎ AcraConnector ↔︎ AcraServer ↔︎ SQL database
AcraConnector is deprecated since 0.91.0 and is not available since 0.92.0.
AcraWriter is available in Acra Enterprise Edition only.
A combination of methods above. Application uses AcraWriter SDK to encrypt data on application side. App uses strong transport encryption provided by AcraConnector to connect to AcraServer to send encrypted data. Then AcraServer sends data to the database.
When data is required in a plaintext, AcraServer decrypts it and sends (protected) via AcraConnector back to the app.

When to use #
When client-side application works in a hostile environment. Client-app performs data encryption and then uses strong transport encryption to send data to the AcraServer / database.
Which components to use #
AcraWriter, AcraServer, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and AcraConnector.
Writing #
Application [AcraWriter] → AcraConnector → AcraServer → SQL database
Application locally encrypts sensitive data using AcraWriter. The app is responsible for accessing Acra’s encryption keys. Then the app sends data to the database directly or to the AcraServer. Encrypted data is sent to AcraServer through AcraConnector that protects it using TLS or Themis Secure Session.
Reading #
Application → AcraConnector → AcraServer → SQL database → AcraServer → AcraConnector → Application
Application requests data from a database through AcraServer. AcraServer transparently decrypts/detokenizes/unmasks data and passes it safely to the application using AcraConnector.
Using AcraConnector and AcraTranslator #
App ↔︎ AcraConnector ↔︎ AcraTranslator, App ↔︎ Datastore
AcraConnector is deprecated since 0.91.0 and is not available since 0.92.0.
Similar to the classic scenario the simplest dataflow with AcraTranslator, but the application uses AcraConnector for transport encryption.

When to use #
When client-side application works in a hostile environment and extra transport security is required.
Which components to use #
AcraTranslator, Key management utilities, Key storage, KMS and AcraConnector.
Writing #
Application → AcraConnector → AcraTranslator → AcraConnector → Application → Datastore
Application knows which fields to encrypt/mask/tokenize. Application sends these fields to AcraTranslator via gRPC or HTTP API. AcraTranslator performs required function and sends protected data back to the app. All data is sent through AcraConnector to protect plaintext data from application to AcraTranslator via TLS or Themis Secure Session.
Reading #
Application → Datastore → Application → AcraConnector → AcraTranslator → AcraConnector → Application
Application reads encrypted data from the storage or the other application and needs to decrypt/demask/detokenize it. Application sends these fields to AcraTranslator via gRPC or HTTP API. AcraTranslator performs required function and sends original data back to the app. All data is sent through AcraConnector to protect plaintext data from application to AcraTranslator via TLS or Themis Secure Session.
Data flow with Zones #
Zones are deprecated since 0.94.0, will be removed in 0.95.0.
Data flow with zones are similar for schemas described above except several additional steps at the beginning:
- Zone generation via acra-addzone utility or AcraServer’s HTTP API.
- Specifying Zone ID in requests to AcraTranslator or inside DB query to database through AcraServer.